Geothermal energy is a form of renewable energy that harnesses the earth’s natural heat to produce electricity. With its potential to provide sustainable power while reducing greenhouse gas emissions, geothermal energy has become an increasingly attractive option for countries seeking to transition to clean energy. However, a major concern for many people is the cost of geothermal energy. How much does geothermal energy cost per kWh? Is it affordable for the average consumer, or is it only viable for large-scale projects? In this article, we will delve into the economics of geothermal energy and explore the factors that influence its cost, as well as its current and future outlook as a viable source of clean energy.
Understanding Geothermal Energy and its Cost-Effective Benefits
Geothermal energy is a renewable energy source that utilizes the earth’s heat to generate electricity. Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite resources, geothermal energy is a virtually inexhaustible source of power. Understanding the unique properties of geothermal energy and its benefits can help us realize its potential as a cost-effective and sustainable alternative to traditional forms of energy.
Here are some key points to consider when understanding geothermal energy and its cost-effective benefits:
- Geothermal energy is reliable and consistent: Unlike wind and solar power, which can be intermittent, geothermal energy provides a consistent and reliable source of power, with minimal fluctuations.
- Geothermal energy is clean and environmentally friendly: Geothermal energy produces no greenhouse gas emissions, making it a clean and sustainable source of power that can help mitigate the effects of climate change.
- Geothermal energy is cost-effective in the long run: While the upfront costs of building a geothermal power plant may be high, the operating costs are much lower than those of fossil fuel power plants. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, geothermal energy can be cost-competitive with fossil fuels in areas with favorable geothermal resources, and can even be cheaper in the long run due to lower maintenance costs.
- Geothermal energy can be used for heating and cooling as well: In addition to producing electricity, geothermal energy can also be used for heating and cooling buildings. In fact, geothermal heat pumps are becoming an increasingly popular way to heat and cool homes and buildings, as they are highly efficient and can save homeowners up to 70% on their heating and cooling bills.
- Geothermal energy has the potential to meet a significant portion of our energy needs: According to the International Energy Agency, geothermal energy could potentially meet up to 3.5% of the world’s electricity needs by 2050, up from just 0.3% today.

Factors Influencing Geothermal Energy Cost per kWh
The cost of geothermal energy varies depending on several factors, including the location of the geothermal resource, the type of power plant used, and the level of government incentives and funding available. Here are some of the key factors that influence the cost of geothermal energy per kWh:
- Resource quality and depth: The quality and depth of the geothermal resource can have a significant impact on the cost of producing electricity. Deeper and hotter resources generally produce more electricity, but they also require more expensive drilling and exploration techniques. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, the cost of drilling a geothermal well can range from $2 million to $10 million, depending on the depth and temperature of the resource.
- Type of power plant: There are two main types of geothermal power plants: binary cycle and flash steam. Binary cycle power plants are more expensive to build, but they are more efficient and can generate electricity from lower-temperature resources. Flash steam power plants, on the other hand, are less expensive to build but require higher temperature resources to be cost-effective. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency, the cost of building a geothermal power plant can range from $2,500 to $7,500 per kW, depending on the type of power plant used.
- Level of government incentives and funding: Incentives and funding from governments can help to reduce the cost of geothermal energy and make it more competitive with other forms of energy. For example, the U.S. federal government provides a production tax credit of 1.1 cents per kWh for electricity produced from geothermal resources. In addition, many countries provide grants, loans, and other forms of financial support to help spur the development of geothermal energy.
- Operational and maintenance costs: While the initial capital costs of building a geothermal power plant can be high, the operational and maintenance costs are generally lower than those of fossil fuel power plants. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, the operational costs of a geothermal power plant are typically between 1 and 3 cents per kWh, compared to 3 to 5 cents per kWh for natural gas power plants.
Overall, the cost of geothermal energy per kWh is influenced by a range of factors, including the quality and depth of the geothermal resource, the type of power plant used, the level of government incentives and funding available, and the operational and maintenance costs of the power plant.
Table: Average Cost of Geothermal Electricity by Region (2019)
| Region | Average Cost (USD cents per kWh) |
| Africa | 6.5-13.2 |
| Asia | 4.9-9.6 |
| Europe | 4.8-11.3 |
| North America | 3.8-8.2 |
| Oceania | 6.8-8.3 |
| South America | 7.1-8.3 |
Comparison of Geothermal Energy Costs with Other Renewable Energy Sources
Geothermal energy is one of the most reliable and cost-effective renewable energy sources available today. Here is a comparison of the costs of geothermal energy with other renewable energy sources.
- Solar Energy – Solar energy is one of the most popular renewable energy sources, and it’s becoming more affordable every day. The cost of solar energy is about 10-12 cents per kWh, which is more expensive than geothermal energy.
- Wind Energy – The cost of wind energy has dropped significantly over the past few years. The current cost of wind energy is around 6-7 cents per kWh, which is less expensive than geothermal energy.
- Hydro Energy – Hydro energy is one of the cheapest renewable energy sources available. The current cost of hydro energy is around 4-6 cents per kWh, which is less expensive than geothermal energy.
Overall, geothermal energy is more cost-effective than solar energy but less cost-effective than wind and hydro energy.
The Economics of Geothermal Energy in Different Regions and Countries
The cost of geothermal energy can vary significantly from region to region and from country to country. Here are some examples of the economics of geothermal energy in different regions and countries.
- Iceland – Iceland is one of the leaders in geothermal energy production. Geothermal energy accounts for over 70% of the country’s total energy consumption, and the cost of geothermal energy in Iceland is around 4-5 cents per kWh.
- United States – The United States is another country with significant geothermal energy resources. The cost of geothermal energy in the United States ranges from 5-10 cents per kWh, depending on the location of the power plant.
- Philippines – The Philippines is a country that heavily relies on geothermal energy. The cost of geothermal energy in the Philippines is around 7-8 cents per kWh.
- Kenya – Kenya is another country with significant geothermal energy resources. The cost of geothermal energy in Kenya is around 7-9 cents per kWh.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does geothermal energy compare to other renewable energy sources in terms of cost?
Geothermal energy is generally more cost-effective than other renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, due to its high capacity factor and relatively low operating costs.
What are some of the factors that influence the cost of geothermal energy production?
Some of the factors that can influence the cost of geothermal energy production include the geological conditions of the site, the size of the power plant, and the cost of drilling and installation.
Are there any government incentives available for geothermal energy projects?
Many governments offer incentives, such as feed-in tariffs or tax credits, to promote the development of geothermal energy projects and reduce the financial risk for investors.
What are some of the environmental benefits of using geothermal energy?
Geothermal energy is a clean and renewable energy source that produces little to no greenhouse gas emissions. It also has a low land-use footprint and does not require water for cooling, making it a more sustainable option than traditional fossil fuel-based energy sources.
What advancements are being made in geothermal technology?
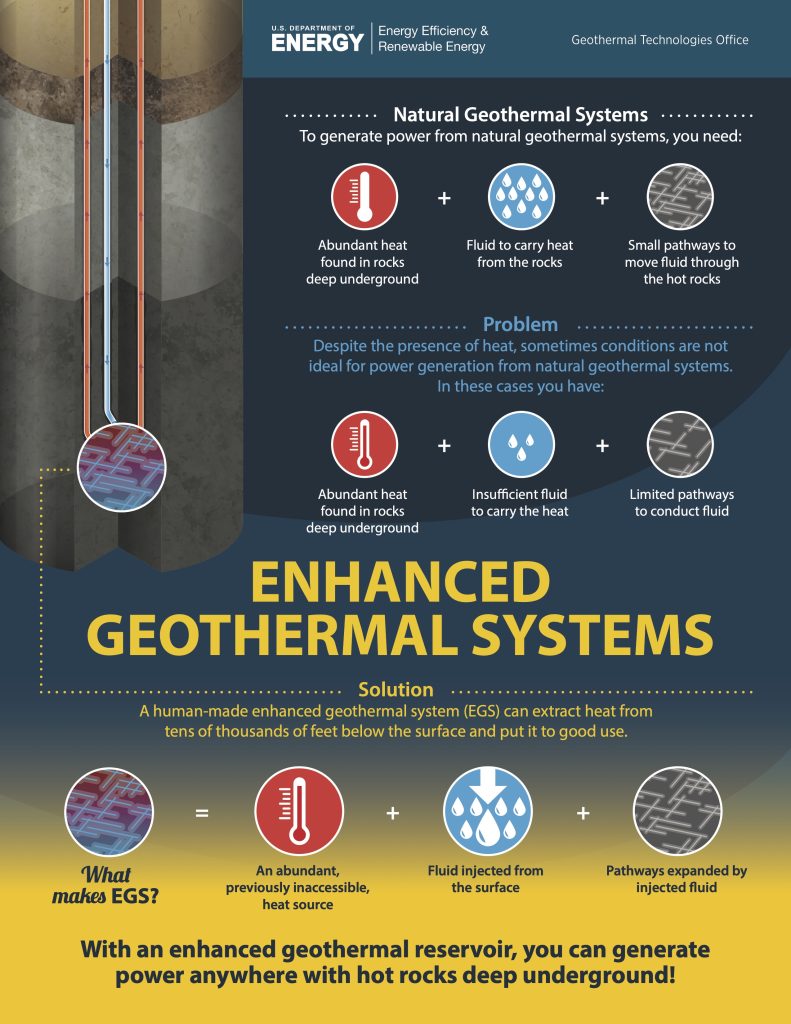
Advancements in geothermal technology include the development of enhanced geothermal systems, which use hydraulic fracturing to create new geothermal reservoirs, as well as the use of binary cycle power plants, which can generate electricity from lower-temperature geothermal resources. These technologies have the potential to increase the accessibility and cost-effectiveness of geothermal energy.
In conclusion, geothermal energy is a promising source of renewable energy that can provide numerous economic and environmental benefits. While the initial installation costs may be high, the long-term cost-effectiveness of geothermal energy, combined with government incentives and advancements in technology, makes it an attractive option for many regions and countries around the world. As we continue to explore alternative energy sources, geothermal energy is a valuable option to consider.


